Cloud computing has seen unprecedented adoption by global businesses as they move towards the new internet paradigm to become better connected. As a result, much innovation has been observed in the Internet of Things (IoT) space like smartphones, self-driving cars, e-surveillance, unmanned drones, etc. As time will progress, more “things” will get connected, largely by wireless technology, which leads us to one of the biggest challenges facing IoT—bandwidth and real-time data processing.
One of the promising solutions emerging in this space is fog computing in IoT.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding “Fog”
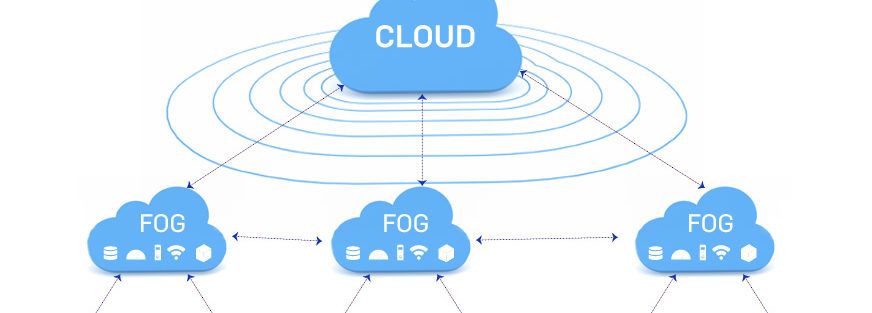
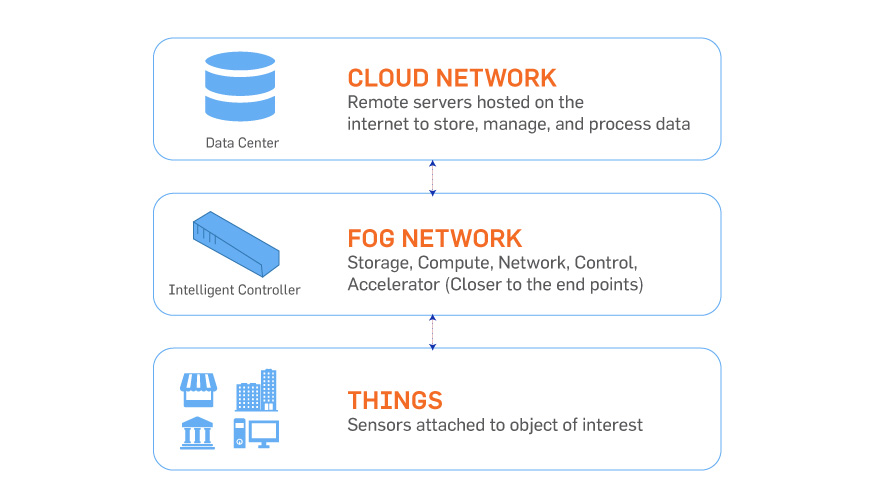
The fog is an extension of cloud-based computing. A horizontal, system-level architecture that distributes computing, storage, control, and networking functions closer to the users along a cloud-to-thing continuum.
What is fog computing? It refers to a decentralized computing model where data is processed at or near the source of data generation, rather than relying solely on cloud servers.
Fog enables us to build solutions around:
- Location awareness
- Mobility
- Wide geographical distribution
- Low latency (delay for information to go from point A to point B)
- Wireless access
This makes fog computing in IoT highly suitable for applications requiring instant decision-making and local intelligence—especially in sectors like surveillance, healthcare, and smart cities.
Smart Fog
Fog is not simply adding layers between the cloud and the surface. It will act as an enabler for smart IoT devices, and the new capabilities it will make possible are:
- Sharing resources from one device to another
- Taking real-time decisions
- Contextual data (available locally) for customized intelligence enhancing user experience
- Autonomous networks that operate locally and can take decisions like saving energy and network bandwidth, improving data security, reducing latency, etc.
- Streamlining online-to-offline processes by leveraging the physical proximity of customers for better authentication and cross-sell opportunities
This is the role of fog computing in IoT—making smart systems even smarter through local decision-making and faster responsiveness.
E-surveillance and Fog
Surveillance cameras are being deployed worldwide by retail outlets, smart homes and cities, manufacturing enterprises, etc. in order to secure things, people and places. They are heavily relying on camera sensors to detect unauthorized entry, pilferage, safety, reliability, and efficiency.
These cameras are capable of generating terabytes worth of information in a single day. Traditional cloud networks are unavailable to handle this massive information as they aren’t scalable, and the sheer cost makes it unfeasible. Besides, it is impractical to transfer all this data to the cloud to gain real-time insights.
Another point to consider is that security needs to be local. Real-time monitoring and detection of irregularities strictly needs low latency on surveillance systems; making timeliness paramount for both detection and response.
This is where the role of fog computing in IoT becomes crucial. Fog deployments provide an opportunity to address the above concerns by moving the compute decision-making device closer to the endpoint.
We leverage fog computing in IoT to crunch data near the endpoints and deliver the filtered data relevant for trend analysis and forensics to the cloud. This ensures faster reaction, greater resilience, and more efficient bandwidth usage.
Closing Thoughts
As e-surveillance becomes more data-intensive and latency-sensitive, relying solely on cloud infrastructure is no longer practical. What is fog computing in IoT, if not the solution to the biggest challenge facing surveillance today—the need for speed, accuracy, and local decision-making?
In Part 2, we’ll explore how fog computing integrates with AI, edge devices, and predictive analytics to create truly intelligent surveillance ecosystems.
– By George M.J., Sr. Vice-President – Information Technology